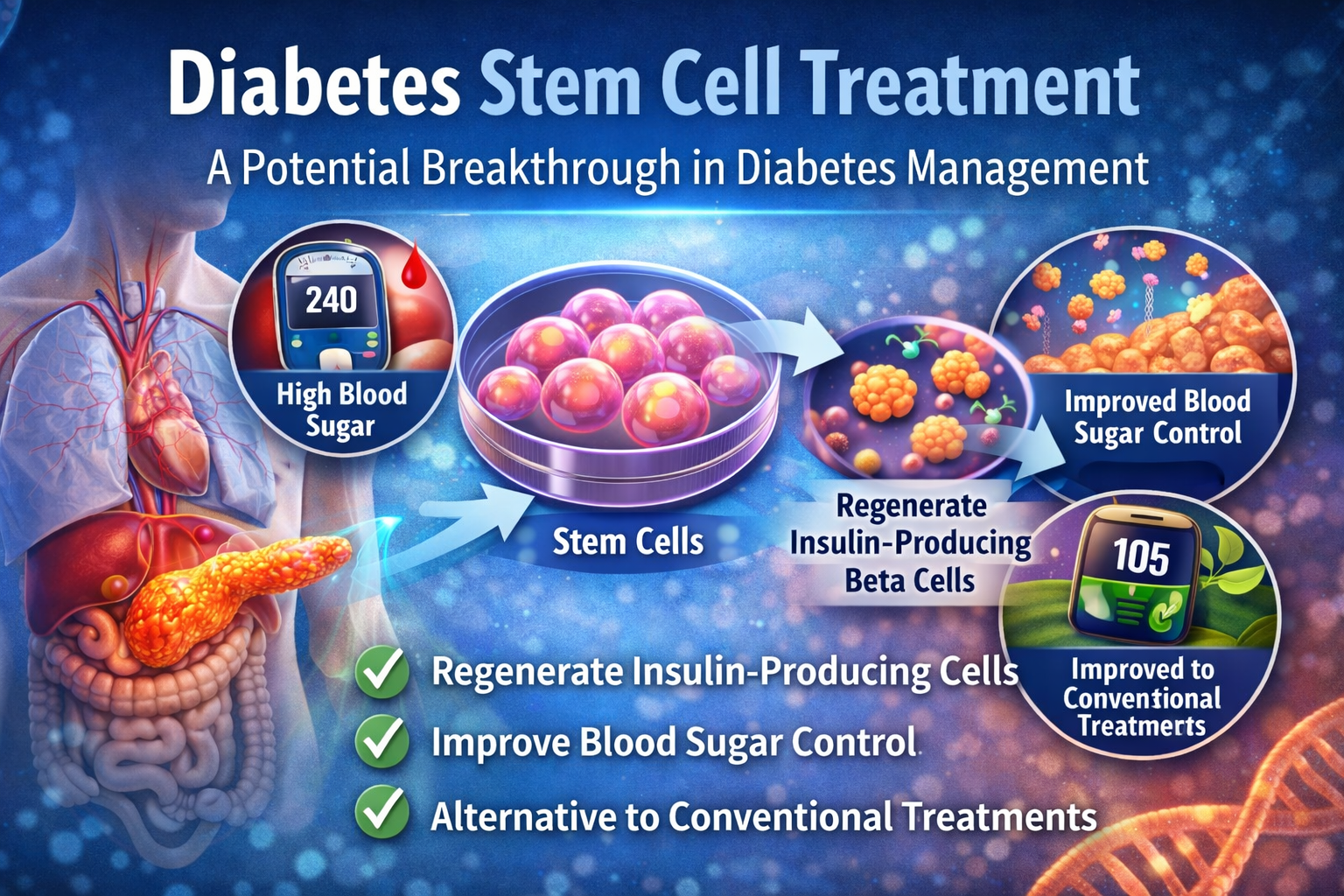
Diabetes Stem Cell Treatment: A Revolutionary Approach to Managing Diabetes
Diabetes has become one of the most common chronic diseases worldwide, affecting millions of people. Traditional treatments for diabetes primarily focus on managing blood sugar levels through medications, insulin therapy, and lifestyle changes. While these methods can be effective, they do not address the root cause of the disease, particularly for Type 1 and advanced Type 2 diabetes. This is where Diabetes Stem Cell Treatment comes into play, offering a potential breakthrough in the management and reversal of diabetes.
Understanding Stem Cell Therapy for Diabetes
Stem cells are unique cells in the body with the ability to develop into various types of cells and repair damaged tissues. In the context of diabetes, stem cells can be used to regenerate the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, which are often destroyed or impaired in diabetic patients. By restoring these cells, the body can potentially regain its natural ability to regulate blood sugar levels, reducing the dependence on external insulin and medications.
Several types of stem cells are utilized in Diabetes Stem Cell Treatment, including:
Embryonic Stem Cells: These cells have the ability to develop into any type of cell in the body, including pancreatic beta cells.
Adult Stem Cells: Found in tissues like bone marrow and adipose tissue, these cells can differentiate into specific cell types and are commonly used in therapeutic applications.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs): These are adult cells reprogrammed to behave like embryonic stem cells, offering a promising alternative without ethical concerns.
How Diabetes Stem Cell Treatment Works
The process of Diabetes Stem Cell Treatment generally involves harvesting stem cells, processing them in a laboratory, and then reintroducing them into the patient’s body. The goal is for the stem cells to target the damaged pancreas, regenerate beta cells, and improve insulin production.
Harvesting Stem Cells: Stem cells can be extracted from the patient’s own body (autologous) or from a donor (allogeneic). Using autologous stem cells reduces the risk of immune rejection.
Stem Cell Cultivation: Once harvested, the stem cells are cultured in controlled conditions to increase their quantity and enhance their ability to develop into pancreatic cells.
Transplantation: The cultivated stem cells are then introduced into the patient’s pancreas through minimally invasive techniques or intravenous infusion.
Regeneration and Monitoring: After transplantation, the stem cells work to regenerate beta cells and improve insulin secretion. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels helps evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment.
Benefits of Diabetes Stem Cell Treatment
Diabetes Stem Cell Treatment offers several advantages over conventional treatments:
Potential Reversal of Diabetes: Unlike medications that only manage symptoms, stem cell therapy targets the root cause by restoring pancreatic function.
Reduced Dependence on Insulin: Patients undergoing successful stem cell therapy may require less or no external insulin.
Minimal Side Effects: Stem cell therapy is generally considered safe, especially when using autologous stem cells.
Improved Quality of Life: By stabilizing blood sugar levels naturally, patients can experience fewer complications and improved overall well-being.
Current Research and Clinical Trials
The field of Diabetes Stem Cell Treatment is rapidly evolving. Numerous clinical trials are ongoing worldwide to evaluate the safety and efficacy of stem cell therapy for both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. Early studies have shown promising results, with patients demonstrating improved insulin production and better blood sugar control.
Research is also focused on enhancing stem cell therapy outcomes by combining it with other advanced techniques such as gene therapy, tissue engineering, and immunomodulation. These innovations aim to further increase the success rate of diabetes reversal and long-term sustainability of the treatment.
Risks and Considerations
While Diabetes Stem Cell Treatment is promising, it is important to consider potential risks:
Immune Reactions: Allogeneic stem cells may trigger immune responses if not carefully matched.
Tumor Formation: Although rare, there is a risk of uncontrolled cell growth if stem cells are not properly regulated.
High Cost: Stem cell therapy can be expensive and may not be widely accessible.
Need for Expertise: The procedure requires highly specialized medical expertise and laboratory facilities.
Patients considering Diabetes Stem Cell Treatment should consult experienced endocrinologists and stem cell therapy centers to understand the suitability and potential outcomes.
Future of Diabetes Stem Cell Treatment
The future of Diabetes Stem Cell Treatment looks highly promising. With ongoing research, technological advancements, and a better understanding of stem cell biology, it is expected that this therapy could become a standard treatment option for diabetes. The goal is not only to manage diabetes effectively but also to achieve a potential cure by regenerating pancreatic function.
Researchers are also exploring personalized stem cell therapies tailored to individual patient needs, improving the efficacy and reducing complications. As the field grows, it may offer hope to millions suffering from diabetes, enabling them to lead healthier and more independent lives.
Conclusion
Diabetes Stem Cell Treatment represents a revolutionary approach to diabetes management, focusing on repairing and regenerating the pancreas rather than just controlling symptoms. While still under extensive research and clinical evaluation, early results show significant potential in improving insulin production, lowering blood sugar levels, and enhancing patients’ quality of life.
For anyone seeking alternatives to conventional diabetes management, stem cell therapy offers hope and a glimpse into the future of regenerative medicine. With continued advancements, Diabetes Stem Cell Treatment could transform the way diabetes is treated, offering long-term solutions and improved outcomes for patients worldwide.